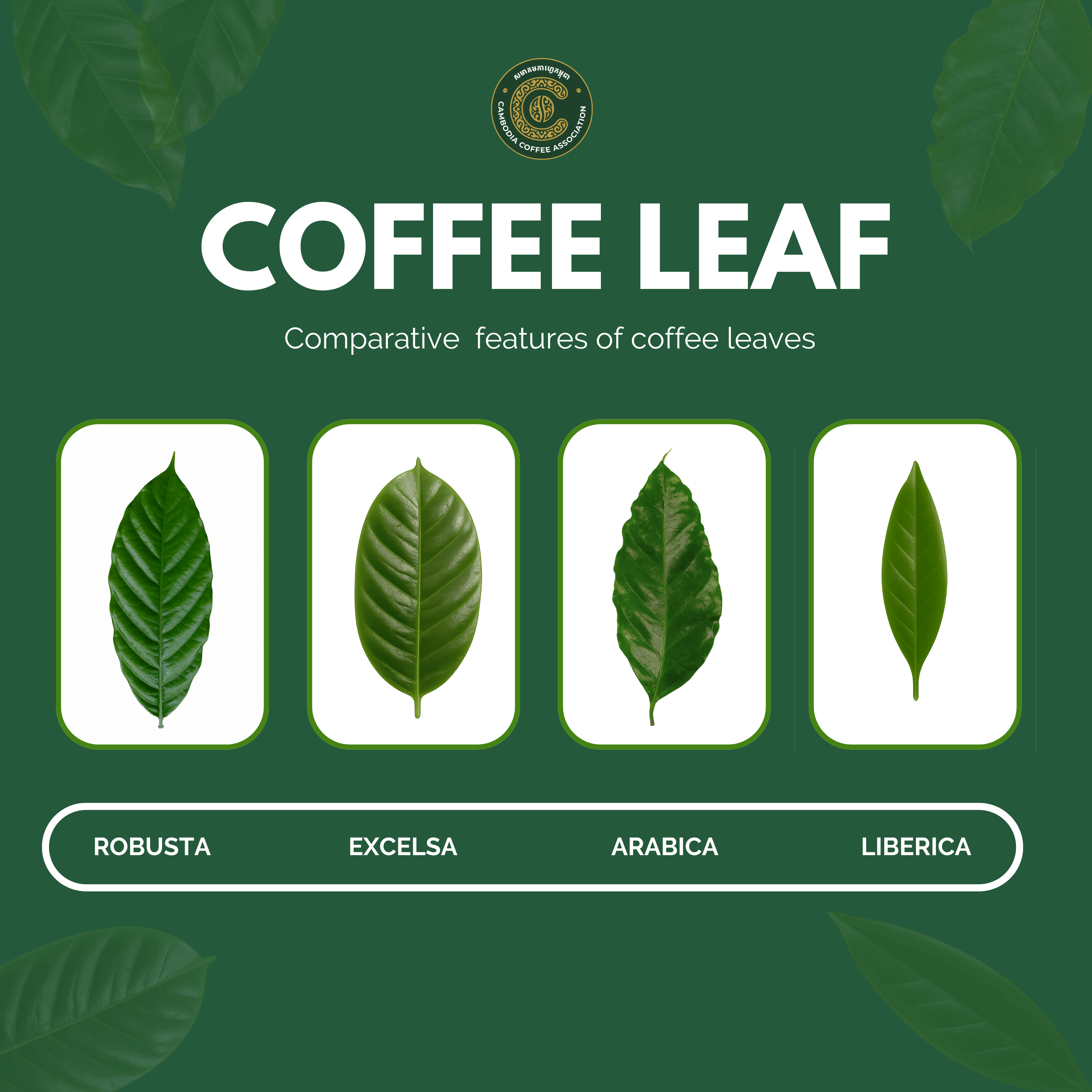
Coffee leaves vary across species, and their unique characteristics help farmers, researchers, and enthusiasts distinguish between different types of coffee plants. Below are the comparative features of the four main commercially recognized species: Arabica, Robusta, Liberica, and Excelsa.
1. Size and Shape
-
Arabica (Coffea arabica): Medium to large, oval-shaped, smooth edges, often slightly wavy.
-
Robusta (Coffea canephora): Medium-sized, narrower and more elongated than Arabica, with thicker edges.
-
Liberica (Coffea liberica): Very large, asymmetrical, and leathery leaves with prominent veins.
-
Excelsa (Coffea excelsa): Medium to large, somewhat similar to Liberica but slightly smaller and thinner.
2. Color and Texture
-
Arabica: Light green, thin, and delicate texture.
-
Robusta: Dark green, thick, and tough leaves, adapted to heat and pests.
-
Liberica: Dark glossy green, leathery and very tough, built for humid tropical climates.
-
Excelsa: Green to dark green, somewhat leathery but less glossy than Liberica.
3. Vein Pattern
-
Arabica: Fine, less pronounced veins, giving a smooth appearance.
-
Robusta: Veins are bold and visible, contributing to a rugged look.
-
Liberica: Strongly pronounced veins with asymmetry between left and right halves of the leaf.
-
Excelsa: Prominent veins but more balanced than Liberica, slightly curved patterns.
4. Glossiness
-
Arabica: Moderate gloss, more matte in appearance.
-
Robusta: Glossy surface, reflecting resilience in hot and humid climates.
-
Liberica: Highly glossy, leathery sheen.
-
Excelsa: Mild to medium gloss, not as shiny as Liberica.
5. Growth Habit & Adaptation
-
Arabica: Prefers cooler, higher altitudes (1,000–2,000m); leaves show vulnerability to pests/diseases.
-
Robusta: Thrives in lower altitudes and hotter climates; tougher leaves with natural resistance.
-
Liberica: Grows well in lowland tropical regions; leaves adapted to humid, swampy areas.
-
Excelsa: Often grown in similar conditions as Liberica; leaves show adaptability to varied soil and climate.
Understanding these differences not only helps identify coffee species in the field but also highlights how each plant has evolved to thrive in its environment — from the delicate Arabica to the towering Liberica.
